The earliest forms of AI features in mobile devices can be traced back to the early 2000s, with the introduction of basic voice recognition and predictive text capabilities. However, more advanced AI features began to emerge in smartphones around the late 2000s and early 2010s.
Brief History
Voice Recognition and Virtual Assistants
One of the earliest and most prominent AI features in mobile devices was voice recognition, which led to the development of virtual assistants:
- Siri: Introduced by Apple in 2011 for the iPhone 4S, Siri was one of the first widely adopted virtual assistants. It used natural language processing to understand and respond to voice commands.
- Google Voice Search: Launched in 2008 for the iPhone, it later evolved into Google Now in 2012 and eventually became Google Assistant in 2016.
Predictive Text and Autocorrect
These features used basic machine learning algorithms to improve text input:
- T9 (Text on 9 keys): Introduced in the late 1990s for feature phones, it used predictive text technology to guess words based on key presses.
- Swype: Launched in 2009, it used AI to predict words as users swipe their fingers across the keyboard.
Image Recognition and Processing
Early forms of AI-powered image processing began to appear in smartphones in the early 2010s:
- Face detection: Used for focusing and image organization.
- Automatic scene recognition: Helped optimize camera settings based on the environment.
Personalization and Recommendations
Basic AI algorithms were used to provide personalized experiences:
- App recommendations: Suggesting apps based on usage patterns.
- Content recommendations: Offering personalized news feeds and content suggestions.
Battery Optimization
Early forms of AI were used to analyze usage patterns and optimize battery life:
- Adaptive Battery: Introduced by Google in Android 9 Pie (2018), it used machine learning to prioritize battery power for frequently used apps.
While these early AI features may seem rudimentary compared to today’s advanced AI-powered smartphones, they laid the foundation for the more sophisticated AI capabilities we see in modern devices. The integration of AI in mobile devices has accelerated rapidly in recent years, with the introduction of on-device machine learning, advanced natural language processing, and generative AI features[1].
As technology continues to evolve, mobile applications are at the forefront of innovation, integrating advanced AI technologies like Generative AI (GenAI) and Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance user engagement and provide groundbreaking solutions. However, the integration of these technologies also raises significant privacy concerns, particularly as they often rely on cloud computing.
This blog post will explore the future of mobile applications by examining the role of AI, the emerging privacy solutions, and the hybrid approaches that promise a more holistic user experience.
Present in progress
AI Integration in Mobile Applications
The integration of AI technology, such as GenAI, has led to a transformation in the way users engage with mobile applications. GenAI models, PredictiveAI, and CommunicationAI have empowered applications to comprehend and produce human-like text, identify images, and execute complex tasks through voice commands.
Applications like chatbots, virtual assistants, and personalized content recommendations are just a few examples of how AI is creating more engaging and intuitive user experiences.
Enhanced User Engagement
One of the primary benefits of AI integration is the ability to provide personalized experiences.
By analyzing user behavior and preferences, AI can tailor content, recommendations, and interactions to each individual.
This level of personalization not only enhances user satisfaction but also increases engagement and retention.
For instance, streaming services use AI algorithms to suggest movies and shows that align with a user’s viewing history, while e-commerce platforms recommend products based on past purchases and browsing habits.
Intelligent Automation
AI-powered automation is another significant advancement in mobile applications.
Virtual assistants such as Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa harness AI to execute tasks like setting reminders, sending messages, and controlling smart home devices—all through voice commands.
These assistants are continuously improving, becoming more adept at understanding natural language and providing accurate responses.
Moreover, AI-driven automation extends to customer service, where chatbots handle inquiries and provide support, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues.
Advanced Image and Voice Recognition
AI technologies have also revolutionized image and voice recognition capabilities in mobile applications.
Facial recognition systems enhance security by allowing users to unlock their devices and authenticate transactions using their faces.
Similarly, voice recognition enables hands-free operation and accessibility features, making mobile devices more inclusive for users with disabilities.
The integration of these technologies creates a seamless and intuitive user experience, blurring the lines between human and machine interactions.
These integration of AI systems are mostly through cloud platforms. Most apps use OpenAI, Claude, Amazon AI or a mix of other SaaS applications to provide the best possible solution.
Concerning Future
Privacy Concerns and On-Device Solutions
Despite the numerous benefits of AI integration, privacy remains a significant concern. Most AI models, especially LLMs, rely on cloud-based processing, which involves sending user data to remote servers for analysis and response generation. This raises significant concerns about data security and user privacy, as sensitive information becomes vulnerable to potential breaches or misuse.
Data Security Risks
The reliance on cloud-based AI models necessitates the transmission of large amounts of user data to remote servers.
This data includes personal information, interactions, and preferences, which can be susceptible to cyberattacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access.
High-profile incidents of data breaches have heightened user awareness and concern about the security of their data, prompting calls for more robust privacy measures.
On-Device AI Models
To address these concerns, developers are working on smaller LLMs that can operate directly on devices, thereby minimizing the need to transmit data to the cloud.
These on-device models process data locally, reducing the risk of data exposure and enhancing user privacy.
While these models offer improved privacy, they are currently limited in their capabilities compared to their cloud-based counterparts.
The limited computational power and storage capacity of mobile devices create challenges for implementing sophisticated AI models directly on the device.
Nonetheless, ongoing advancements in this area hold promise for more robust and private AI solutions in the future.
On Device AI Examples:
- General AI:
- GenAI:
Hybrid Approaches: The Best of Both Worlds
Recognizing the limitations and benefits of both cloud-based and on-device AI models, companies like Apple are pioneering hybrid approaches to AI integration. Apple’s strategy, known as Apple Intelligence, combines on-device models with cloud-based services from providers like OpenAI.
Apple Intelligence
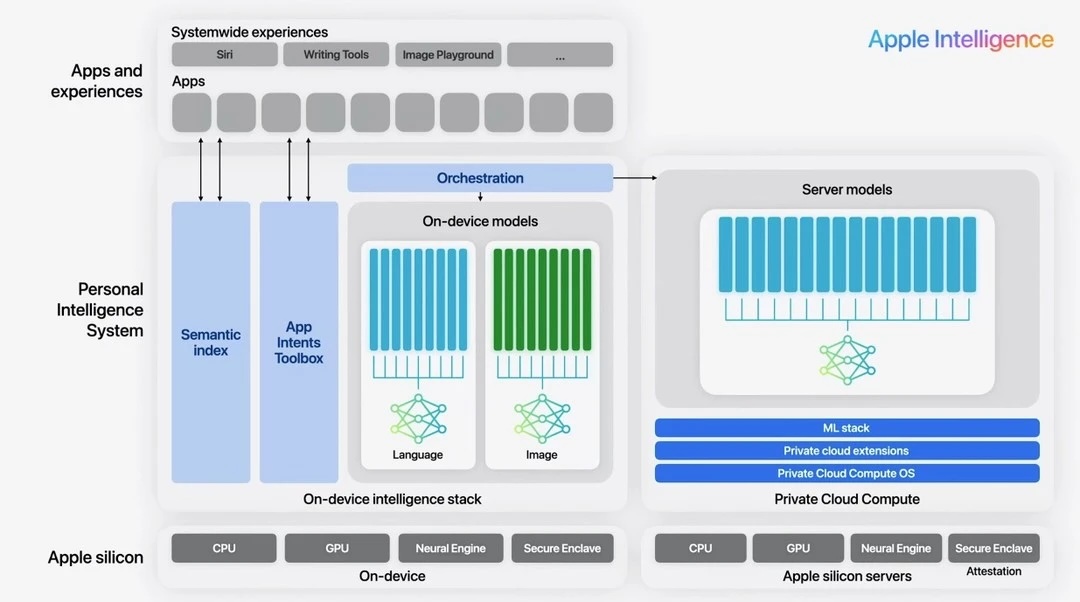
Apple Intelligence exemplifies a hybrid approach that leverages the strengths of both on-device and cloud-based AI models.
This strategy balances on-device models for immediate processing with cloud-based models for complex tasks, enhancing functionality while safeguarding privacy.
For example, voice commands and simple tasks can be handled locally on the device, ensuring quick responses and preserving user privacy.
Meanwhile, more resource-intensive operations, such as advanced natural language processing, are offloaded to cloud servers, maximizing computational efficiency.
Google ASTRA

Google’s Project Astra aims to utilize both on-device and cloud-based models to deliver its advanced AI capabilities.
This hybrid approach allows Astra to leverage the power of cloud computing for complex tasks while maintaining privacy and responsiveness through on-device processing[9][10].
By combining local and remote resources, Astra can offer real-time, context-aware responses across various devices, from smartphones to smart home gadgets[10].
This dual-model strategy enables Astra to balance performance, privacy, and battery life considerations, making it a versatile AI assistant for everyday use[11].
Seamless Integration
The hybrid approach enables mobile applications to seamlessly integrate voice, images, and text, creating a more immersive and intuitive interaction for users.
Consider a scenario where a user photographs an item. The app then not only identifies the object but also offers comprehensive information and purchase options.
This level of integration would be challenging to achieve solely with on-device or cloud-based models.
The hybrid model bridges this gap, offering a comprehensive and secure user experience that combines the best of both worlds.
Conclusion
The future of mobile applications lies in the intelligent integration of AI technologies, which promise to revolutionize user experiences through enhanced capabilities and personalization.
However, the journey towards this future must also address the significant privacy concerns that come with cloud-based AI models.
Emerging solutions like on-device LLMs and hybrid approaches exemplified by Apple’s Apple Intelligence offer promising pathways to balance functionality and privacy.
As these technologies continue to evolve, we can look forward to a new era of mobile applications that provide a holistic and secure experience, seamlessly blending voice, images, and text to meet the diverse needs of users.
- [1] https://blogs.idc.com/2024/07/05/the-rise-of-gen-ai-smartphones/
- [2] https://www.cnet.com/tech/mobile/ai-is-changing-our-phones-and-its-just-getting-started/
- [3] https://www.algolia.com/blog/ux/mobile-apps-and-mobile-app-search-the-past-present-and-future/
- [4] https://www.cnbc.com/2024/08/13/google-pixel-9-phones-first-ai-powered-android-update-announced.html
- [5] https://www.forbes.com/sites/gilpress/2016/12/30/a-very-short-history-of-artificial-intelligence-ai/
- [6] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Timeline_of_artificial_intelligence
- [7] https://www.textmagic.com/blog/smartphone-history-from-the-first-cell-phone-to-the-iphone-and-beyond/
- [8] https://www.qualcomm.com/news/onq/2024/04/beyond-smart-the-rise-of-generative-ai-smartphones
- [9] https://www.talentelgia.com/blog/google-project-astra/
- [10] https://play.ht/blog/project-astra/
- [11] https://www.zdnet.com/article/i-demoed-googles-project-astra-and-it-felt-like-the-future-of-generative-ai-until-it-didnt/
- [12] https://www.engadget.com/google-project-astra-hands-on-full-of-potential-but-its-going-to-be-a-while-235607743.html
- [13] https://www.sify.com/ai-analytics/googles-project-astra-an-overview-of-future-ai-assistants/
- [14] https://thegadgetflow.com/blog/everything-we-know-about-googles-project-astra-so-far/
- [15] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qjgeFtxN9iw
- [16] https://deepmind.google/technologies/gemini/project-astra/
- [17] https://www.nomtek.com/blog/opportunities-on-device-ai


